Many people know collagen as an injectable for wrinkles or as an expensive component of their skin care products. What many people don’t know is that collagen is the basic building block of your entire body. Your body is 30 percent protein, and of that 30 percent, 90 percent is collagen.1 Collagen is a short-chain amino acid comprising primarily glycine and proline. Derived from the Greek word “kola,” meaning, “glue,” this sticky substance makes up a large component of not only hair, skin, and nails but also muscles, tendons, ligaments, and bone. A hard, insoluble, fibrous protein, collagen is what gives these body parts their strength and structure.2 There are 16 types of collagen, but types I, II, and III account for 90 percent of it.
Typically, we can make collagen ourselves, but several factors can affect the production of this essential protein. For example, increased sugar, stress, sunlight, smoking, and autoimmune disorders all slow the production of collagen. In addition, the normal aging process, including hormonal changes such as menopause, can directly affect the body’s ability to produce collagen. Fibroblasts (cells that make up collagen) become less active, thicker, and easier to break with age, so the collagen percentage in the body starts not just to drop but to plummet. Studies show that collagen production starts slowing around age 25-30 and decreases 1 percent per year after that.3 Combine this natural drop with the external factors affecting collagen production in our bodies, and it is a recipe for disaster.
Another factor contributes to the reduction of collagen in our diet: nutrition. Our ancestors subscribed to a “whole animal” nutrition philosophy. More of the tendons, cartilage, and even bone were consumed. These parts of the animal, of course, were loaded with collagen. Now, I want you to picture a naked, boneless breast of chicken sitting in your grocery cart. See the problem? We are not consuming anywhere near as much collagen as we used to. This is a problem.
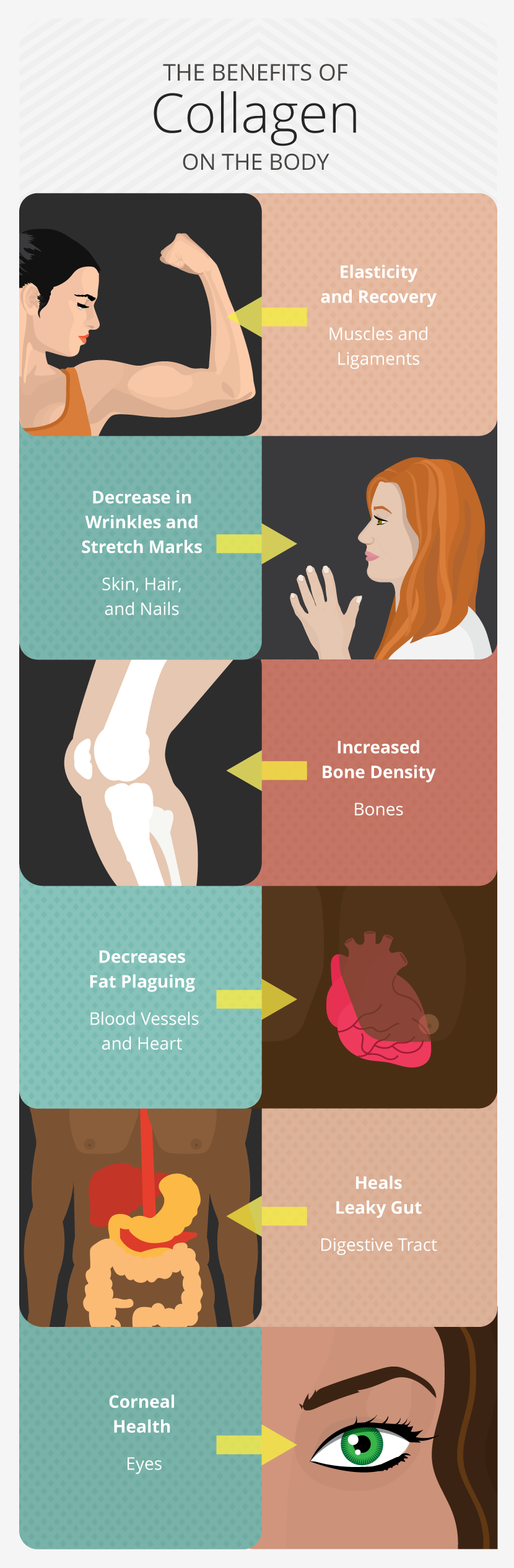
What Parts of our Body Rely on Collagen?
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Skin
- Bone
- Blood vessels
- Digestive tract
- Corneas
- Heart
- Gallbladder
- Hair
- Nails
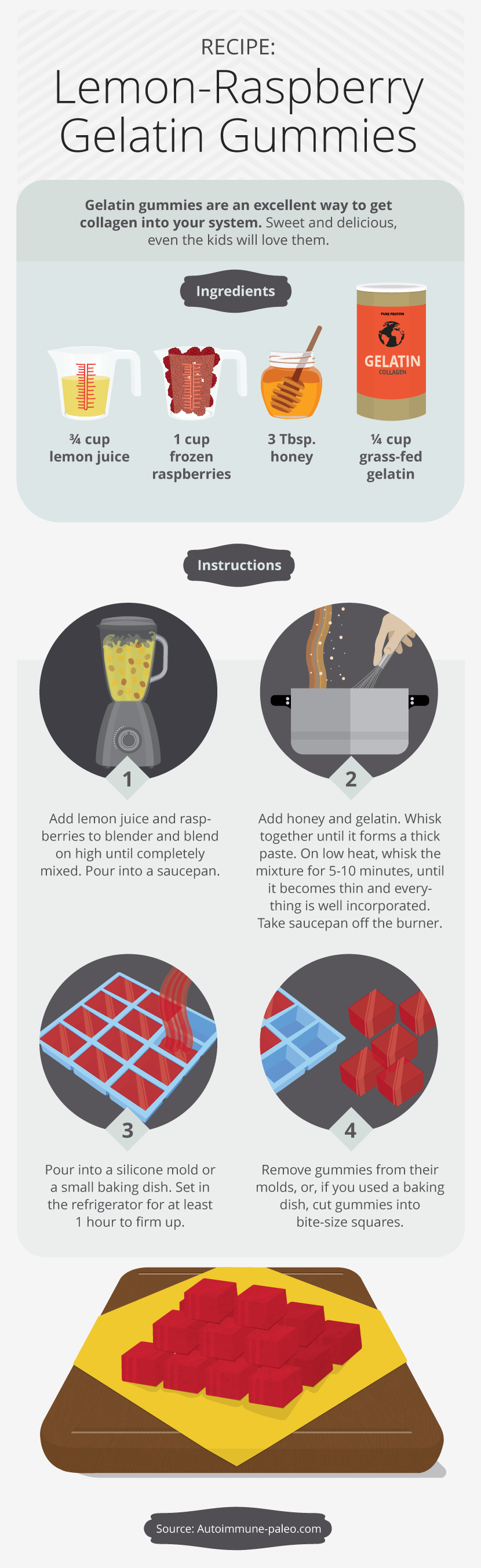
Because we know that this key component of the human structure decreases over time, it makes sense that we need to supplement regularly to support the ongoing optimal function of the body’s many processes controlled by collagen. Before we get to that, there is one thing we should go over first. Many people mistake collagen for gelatin. Let’s set the record straight on the difference between the two. Collagen, as you have learned above, is a short-chain amino acid that is insoluble and makes up many parts of the human body. We know that collagen is in the tendons, ligaments, and bone of animals. We also know that, today, few people actually eat those parts. When you cook these parts, gelatin is released. You can think of gelatin as cooked, heated, or broken-down collagen.4 Consider bone broth. Bone broth is the best example of the transformation of collagen into gelatin. Collagen and gelatin are essentially the same product with the same amino acid makeup, and they work in the body in a similar way.
One more thing must be discussed. At the beginning of this article, I drew your attention to the fact that many know collagen as a superficial skin therapy. Many high-end skin-care lines tout collagen as a key component. Often, they also say that their collagen is plant-based. Let me clear something up. There is no such thing as a plant-based collagen. Plants do not contain any collagen. Second, applying collagen to the surface of the skin has no effect. The proteins are too big to pass through the skin barrier. It is important to know that the only way for collagen make your skin look better is to take it internally as food or as a supplement.
Collagen has several unexpected benefits beyond the skin.
The Six Surprising Benefits of Collagen
- Aids muscle recovery and injury prevention in athletes: The proper amount of collagen in the body can create great elasticity in the tendons and ligaments and can help muscle metabolize and recover more efficiently after workouts.5
- Releases fat from artery walls: We need healthy, scrubbed, and clean arteries to stave off heart disease. Collagen helps accomplish this task.
- Helps build DNA strands: Aging is simply our DNA replication slowing down over time. If collagen can assist in this process in any way, it means that time can slow a little, not just on the outside but on the inside as well.
- Increases energy production in cells: Fatigue, disease, and dysfunction in the body can occur when our cells are not working at their optimal potential. Collagen gives those cells a little energy boost.
- Helps to heal the digestive tract and repair leaky gut: Many say that life and health start at the gut lining. If the gut lining is not absorbing food correctly, it opens us up to a whole host of problems. Collagen helps rebuild, soothe, and heal angry intestines. This may be more valuable than you can imagine.
- Helps alleviate osteopenia: Osteoporosis is one of the leading health issues in aging women. Studies suggest that the addition of collagen to the diet may slow the bone loss cycle, which means that women can stay more active and not fear broken bones resulting from density issues.
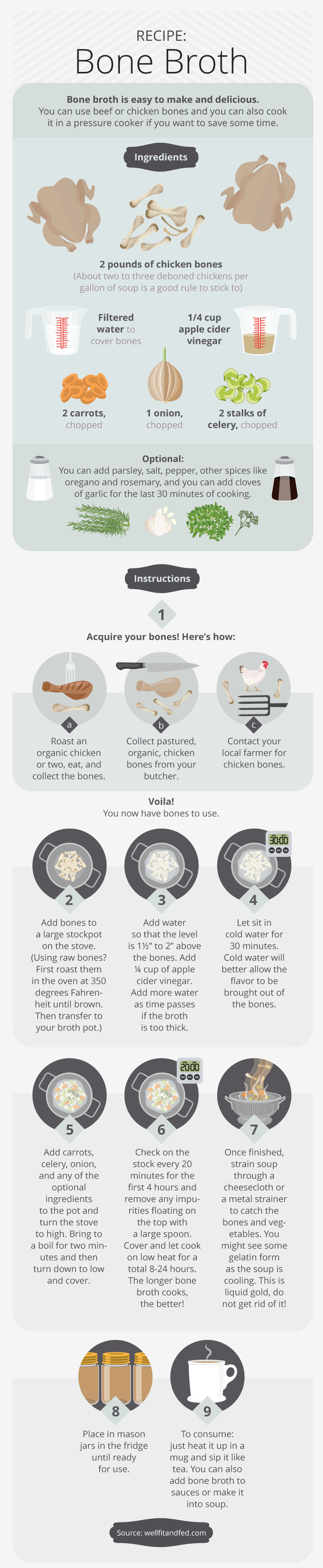
Now that you are convinced about the benefits of collagen, how do you get it into your diet? Obviously, eating the skin, tendons, and small bones of the meats in your diet is an option. Drinking bone broth, however, might be more palatable to most. Bone broth is easy to make at home and is loaded with protein and nutrients. You can also add a collagen supplement to your coffee or a smoothie. It is important to note that your body absorbs collagen much more readily in the presence of vitamin C, so if you add collagen to a smoothie, make sure to add some fruit or other food containing vitamin C. You can also use gelatin to make gummies, which is one of my favorite ways to get collagen into the body!
Collagen is not just about hair, skin, and nails. Our entire connective system, from gut to bone, relies on collagen for optimal functioning. It is essential that we get quality collagen from our diets everyday. So whether you decide to embrace whole animal nutrition, sip your favorite cup of bone broth, or binge on delicious gummies, make sure you are incorporating collagen as part of your nutrition profile.
Reprinted with permission from our friends at Fix.com/blog
Elderberry Gummies Recipe
Some of the items mentioned in article:
About the author:
 Dr. Heather Denniston is a chiropractor who specializes in pediatrics and pregnancy. She has a certification in wellness chiropractic (CCWP), and is the author of The Three Day Reset, a totally doable food plan that anyone can do and see results. You can read her fitness and nutrition expertise at her blog WELLFITandFED.com.
Dr. Heather Denniston is a chiropractor who specializes in pediatrics and pregnancy. She has a certification in wellness chiropractic (CCWP), and is the author of The Three Day Reset, a totally doable food plan that anyone can do and see results. You can read her fitness and nutrition expertise at her blog WELLFITandFED.com.