According to this study at Rice University 70% of all people have candida colonies in their intestines, mouth or skin. Candida albicans frequently causes superficial infections by invading and damaging epithelial cells, but may also cause systemic infections by penetrating through epithelial barriers.
The Candida albicans that grows in your gut, is kept in line by healthy bacteria that also lives in your gut. If however the balance of bacteria is thrown off by antibiotics, poor diet or prescription meds Candida can over run your system. As the candida infections spreads, the overgrowth releases nasty toxic byproducts into your body causing numerous unpleasant symptoms.

Candida symptoms
Brain Fog-Overgrowth of candida can cause poor memory, difficulty concentrating, inability to focus, poor physical coordination and mood changes.
Chronic Fatigue-This illness is typically characterized by tiredness or fatigue that lasts a minimum of six months. It is accompanied by other symptoms including difficulty concentrating, memory difficulties, sore throat, headaches and joint pain.
Digestive Issues-Lack of healthy bacteria in your digestive tract can cause bloating, cramping, gas, constipation, diarrhea, burping. This ongoing problem can also be a sign of a candida infection.
Mood Irregularities-Candida overgrowth can contribute to anxiety, depression, irritability, panic attacks and frequent mood swings.
Oral Thrush–This yeast infection is caused by candida.
Recurrent UTI’s and VI– Candida may be the root cause of frequent urinary tract and vaginal infections.
Sinus Infections-Can result in post nasal drip, persistent cough, seasonal allergies, congestion and general flu type symptoms. Chronic sinus infections can be indicative of candida infection.
Fungal Infections-Athlete’s foot and nail fungal infections are common. These continued infections could be telling you that you have a systemic candida infection.
Hormonal Imbalances-Inability to lose weight, migraines, water retention, low sex drive, early menopause, these are all linked to candida infection.
Insomnia-Inability to sleep through the night, waking frequently.
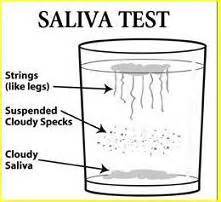
Tests for Candida
There are numerous tests for candida. You might want to start with a basic saliva test at home and then follow up with your doctor to order one of these tests:
Organic acid test– This urine test detects organic waste products created by Candida albicans that are not naturally found in the urine.
Candida antibodies test-This blood test identifies three different antibodies the body produces in response to a Candida infestation. These are the IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies. The levels of these antibodies can signify that a Candida overgrowth is current, or has been present in the recent past.
Comprehensive stool analysis-This stool test is collected at home usually over two to three days to gather an average sample. It is sent to a lab for analysis.
Supplements to help fight yeast overgrowth
Supplements can offer support to the body and provide a healthy balance of microorganisms into your system. Supplements also help to maintain your health and strengthen your immune system.
Antifungals-Antifungals work by destroying the cell walls of candida cells. Some great natural antifungals include; oregano oil, grapefruit seed extract, Pau D’arco, black walnut and caprylic acid.
Digestive enzymes-Enzymes are helpful in assisting your body to break down and digest foods at a much faster rate than would occur on its own. There are eight primary digestive enzymes, each designed to help break down different types of food:
Protease: Digesting protein
Maltase: Converting complex sugars from grains into glucose
Amylase: Digesting carbohydrates
Lactase: Digesting milk sugar (lactose) in dairy products
Lipase: Digesting fats
Phytase: Helps with overall digestion, especially in producing the B vitamins
Cellulase: Breaking down fiber
Sucrase: Digesting most sugars
Probiotics-This good bacteria lines your gut, helps with digestion and prevents infections from spreading. Support your gut bacteria by consuming probiotics that will crowd out candida yeast, boost your immune system and help to regulate gut acidity.

Foods to avoid
Ultimately you need to eliminate any foods that feed yeast and encourage yeast overgrowth. These are foods that include sugar, yeast, starch and foods with added sugar, processed foods, processed meats, candies, sweets and cheeses.
The easiest approach is to change your diet to consume fresh vegetables, fresh meat, nuts, seeds, water and unprocessed foods.
References







