Zinc is a trace mineral that is essential to all forms of life because of its fundamental role in gene expression, cell development and replication. Although severe zinc deficiency is unlikely, being mildly to moderately deficient is not uncommon. In fact the World Health Organization (WHO) reports that globally our deficiency is at 31%.
What is zinc used for in the body?
Zinc stimulates the body to produce antibodies that help to destroy the cold virus, which is why it is commonly found in throat lozenges. Zinc does more than help you with a cold, it plays a critical role in many bodily functions such as:
Cell growth
Gene transcription (the process that allows your cells to read genetic instructions)
Keeps your immune system strong
Stabilizes your metabolic rate
Balances your blood sugar
Maintaining your sense of taste and smell
Protects against oxidative stress

Signs of zinc deficiency
Acne
Depression
Diarrhea
Environmental allergies
Food allergies
Frequent colds
Frequent infections
Impaired sense of taste or smell
Lack of appetite
Leaky gut
Poor neurological function
Rashes
Thinning hair
Weak immune system
Zinc deficiency is linked to diseases such as
Chronic liver disease
Chronic renal disease
Diabetes
Malabsorption syndrome
Malignancy
Other chronic illnesses
Sickle cell disease
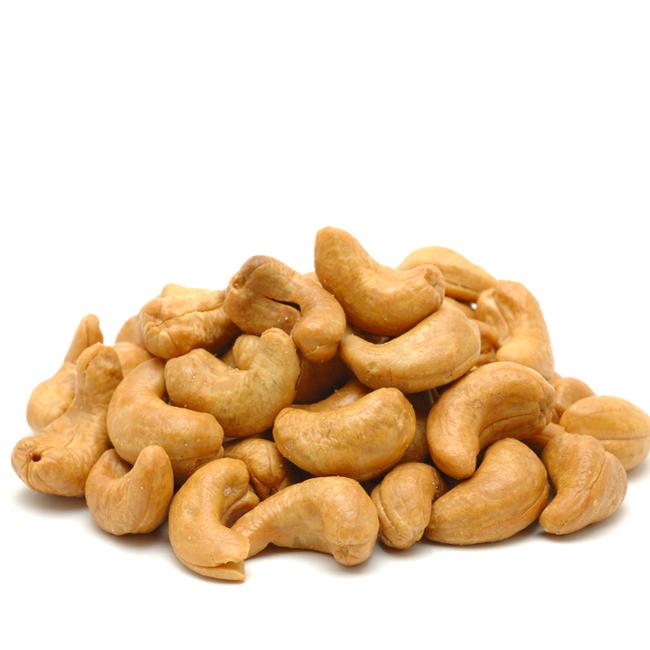

Food sources of zinc
Cashews
Chickpeas (Garbanzo beans)
Crimini mushrooms
Grass-fed beef
Green peas
Kefir
Lamb
Liver
Pumpkin seeds
Spinach
Sea vegetables
Yogurt
Learn how to take a zinc tally test at home.








