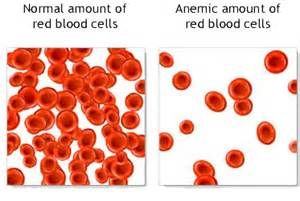
According to the National Institutes of Health’s, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, there are more than 400 types of anemia. Anemia is generally diagnosed by your doctor through family history, physical exam and lab tests.
Anemia is a common blood condition that develops when your blood has a lower than normal number of healthy red blood cells. Anemia can also occur if your red blood cells don’t contain enough hemoglobin. Many cases are mild and easily treated with supplements and nutritional changes, while other forms can be severe and life threatening.
It is important to treat anemia, as severe forms of anemia can damage your brain, heart and other organs in your body. Some forms of anemia can be long term and life threatening if not diagnosed and treated.
In general, the causes of anemia can be divided into three groups:
• Anemia caused by blood loss
• Anemia caused by destruction of red blood cells
• Anemia caused by decreased or faulty red blood cell production
Signs & symptoms of anemia
Anemia symptoms can take time to develop. The most common symptoms are feeling tired and weak. Individuals with anemia may also experience symptoms such as:
• Irritability
• Inability to complete normal daily activities
• Cold hands and feet
• Chest or abdominal pain
• Dizziness
• Pale skin
• Shortness of breath
• Headaches
• Low body temperature
• Irregular heart rate
Risk factors for anemia
Anemia occurs in both men and women, as well as all age, ethnic and racial groups. Certain factors can increase your risk of anemia such as:
-Diet that is low in minerals, vitamins. Especially one lacking in iron, folic acid and B12
-Blood loss from a surgery
-Heavy menstrual periods
-Long term infections
-Family history of inherited anemia, such as sickle cell anemia
-Long term illness such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, liver disease and rheumatoid arthritis
-History of intestinal disorders (such as Crohn’s or Celiac Disease) that affect the absorption of nutrients
Treating and preventing anemia
The treatment you pursue will be based upon the type of anemia you have. Your doctor may suggest dietary changes, supplements such as iron, folic acid, B12 and in more severe cases medications or even a blood transfusion.
Your risk of developing iron deficient or vitamin deficient anemia can be greatly decreased by eating a healthy, organic balanced diet. This would include foods that are rich in iron (such as grass feed beef and dark green leafy vegetables), vitamin B12 (found in meat and dairy), and folic acid (found in citrus juices and dark, green leafy vegetables).
Nutrition tips for anemia
If iron absorption is a problem for you, you may avoid caffeinated drinks, eggs, milk and bran which can interfere with iron absorption.
Consider cooking in cast iron cookware as the cooked food absorbs iron from the pan.
Blackstrap molasses has long been known as a nutritional powerhouse. Blackstrap molasses contains 3.5 mg of iron per tablespoon, blackstrap molasses has been used in folk medicine as a “blood builder” for centuries.
If your anemia is based on nutritional deficiencies consider working with your doctor and a nutritionist to develop an appropriate diet based on your nutritional needs.
| Foods Rich in Iron | Foods Rich in B12 | Foods Rich in Folic Acid |
| Grass fed beef | Beef Liver | Dark Leafy Greens |
| Whole grains | Fish | Asparagus |
| Chicken | Shellfish | Broccoli |
| Fish | Lamb | Citrus Fruits |
| Dark Chocolate | Beef | Beans, Peas & lentils |
| Cocoa Powder | Cheese | Avocado |
| Beans | Whey Powder | Brussel Sprouts |
| Molasses | Eggs | Nuts & Seeds |
| Dried Apricots | Tofu | Cauliflower |
| Prunes | Milk | Beets |
| Kale | Fois Gras (Goose Liver Pate) | Corn |
| Beet Green | Sardines | Celery |
| Swiss Chard | Yogurt | Carrots |
| Chicken Liver | Squash | |
| Nuts | ||
| Leafy Greens |
References:
http://www.myhealthmaven.com/infographics/35-foods-high-in-folic-acid/
http://www.nih.gov/about-nih/what-we-do/nih-almanac/national-heart-lung-blood-institute-nhlbi
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/anemia/
http://www.redcrossblood.org/learn-about-blood/health-and-wellness/iron-rich-foods/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/